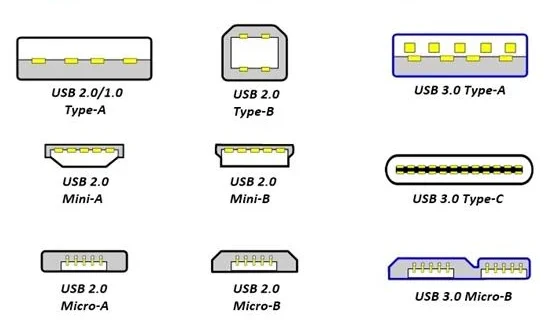
The Universal Serial Bus (USB) has become an essential part of our daily digital interactions. From transferring files to charging devices, USB technology has transformed the way we connect and interact with our gadgets. But how did it all begin? Let’s take a journey through the history of USB and its evolution over the years.
The Birth of USB
Before USB, connecting peripherals to computers was a cumbersome process involving multiple ports and various types of connectors like serial and parallel ports. In 1996, a group of technology companies including Intel, IBM, Microsoft, and Compaq collaborated to develop a universal standard for connecting devices efficiently. This effort resulted in the first USB specification: USB 1.0.
USB 1.0 and 1.1 (1996-1998)
- Introduced to standardize connections and improve plug-and-play functionality.
- Data transfer speed: 1.5 Mbps (Low Speed) and 12 Mbps (Full Speed).
- USB 1.1 (1998) refined the standard, improving device compatibility.
USB 2.0: The Game Changer (2000)
USB 2.0 was a significant leap forward, offering higher data transfer speeds and enhanced device support.
- Data transfer speed: 480 Mbps (High Speed).
- Allowed multiple devices (printers, external hard drives, keyboards, etc.) to connect via USB hubs.
- Became the industry standard for more than a decade.
USB 3.0 and Beyond: Faster and More Efficient
USB 3.0 (2008)
- Introduced SuperSpeed USB with 5 Gbps data transfer rates.
- Improved power efficiency and allowed devices to send and receive data simultaneously.
- Recognizable by its blue-colored ports.
USB 3.1 (2013)
- Boosted speeds up to 10 Gbps.
- Introduced the USB Type-C connector, offering a reversible design for easier plug-in.
USB 3.2 (2017)
- Enhanced data transfer rates up to 20 Gbps.
- Allowed multiple data lanes for increased efficiency.
USB4 (2019-Present)
- Based on Thunderbolt 3 technology, offering speeds up to 40 Gbps.
- Supports multiple display connections, data transfers, and power delivery over a single port.
- Exclusively uses USB Type-C.
The Impact of USB on Technology
USB technology revolutionized connectivity by:
- Simplifying device connections with a universal standard.
- Enhancing data transfer speeds over time.
- Eliminating the need for multiple proprietary cables.
- Supporting power delivery, making charging more convenient.
Future of USB
With USB4 and USB4 v2 on the horizon, future developments promise even faster speeds, better power efficiency, and universal compatibility. As the world moves toward wireless technologies, USB remains a crucial standard in connecting devices efficiently.
Conclusion
From its humble beginnings in 1996 to becoming the backbone of modern device connectivity, USB has continuously evolved to meet the demands of technology. Whether it’s transferring files, charging devices, or connecting peripherals, USB remains an indispensable part of our digital lives.

